Arm Muscles
The arm muscles are divided into two compartments:
1. The anterior (flexor) compartment which consists of:
- Biceps brachii
- Brachialis
- Coracobrachialis muscles.
The muscles in this compartment primarily bring the arm towards the body at the shoulder joint and bend the forearm at the elbow joint. Additionally, they assist in bending the shoulder joint and rotating the forearm outward.
2. The posterior (extensor) compartment includes the:
- Triceps brachii
- Anconeus muscles
These muscles mainly straighten the forearm at the elbow joint, but they also contribute to weakly extending and bringing the arm towards the body.
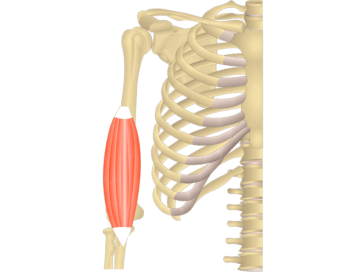
The biceps brachii is a muscle located in the upper arm. It has two heads (hence “biceps”), a long head, and a short head. The primary function of the biceps brachii is elbow flexion, allowing you to bend your arm. It also plays a role in forearm supination, turning the palm upward.
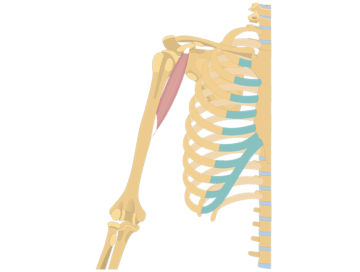
The coracobrachialis is a muscle located in the upper arm, beneath the biceps brachii. Its primary function is to assist in shoulder flexion, allowing you to raise your arm forward. The coracobrachialis also plays a role in shoulder adduction, helping to bring the arm down from a raised position.
The triceps brachii is a muscle located in the upper arm. It has three heads (hence “triceps”)—a long head, lateral head, and medial head. The primary function of the triceps brachii is elbow extension, allowing you to straighten your arm. It plays a crucial role in pushing movements, such as pushing objects away from the body or performing triceps-dominant exercises like push-ups and dips.
Anconeus Muscle
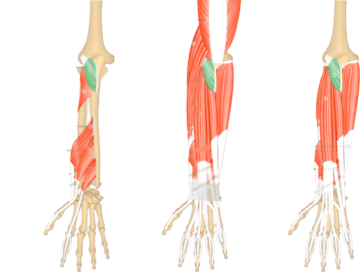
The anconeus is a small muscle located on the back of the elbow joint. Its primary function is to assist in elbow extension, supporting the triceps brachii in straightening the arm. The anconeus muscle also plays a role in stabilizing the elbow during various movements and is involved in activities that require pushing and extending the forearm.
The brachialis is a muscle located in the front of the upper arm, beneath the biceps brachii. Its primary function is elbow flexion, allowing you to bend your arm. The brachialis is essential for various movements that involve lifting and bending the forearm, and it works in conjunction with the biceps brachii to perform these actions.