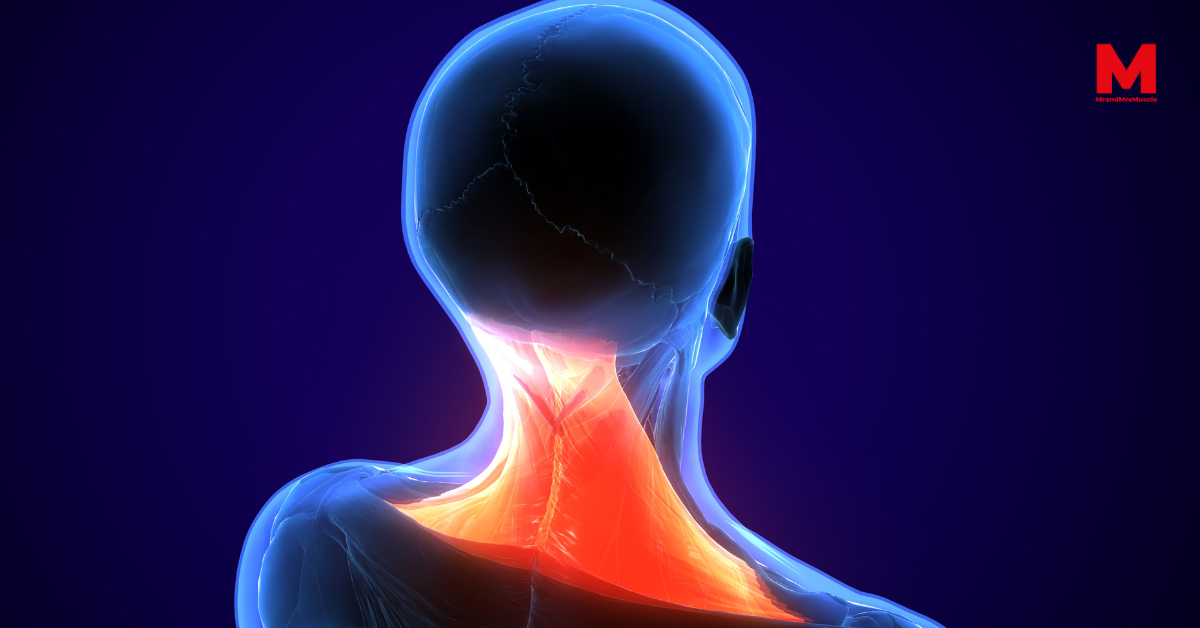
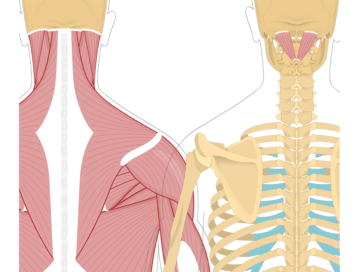
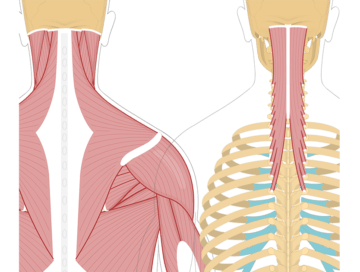
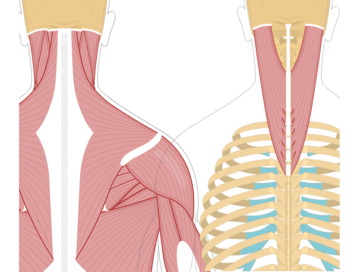
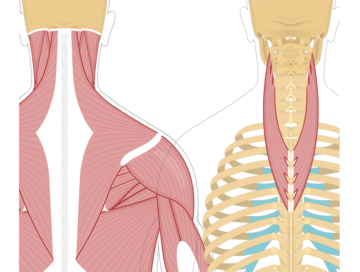
Head and Neck Muscles
These muscles can be further divided into the following subgroups:
- Superficial muscles located beneath the skin: Platysma and sternocleidomastoid.
- Suprahyoid muscles situated above the hyoid bone: Digastric, mylohyoid, geniohyoid, and stylohyoid.
- Infrahyoid muscles located below the hyoid bone: Sternohyoid, omohyoid, sternothyroid, and thyrohyoid.
- Prevertebral muscles positioned anterior to the cervical spine: Rectus capitis anterior, rectus capitis lateralis, longus capitis, and longus colli.
- Pharyngeal muscles, including superior, middle, and inferior pharyngeal constrictors, as well as stylopharyngeus and salpingopharyngeus.
- Laryngeal muscles, such as cricothyroid, posterior cricoarytenoid muscle, lateral cricoarytenoid, thyroarytenoid, oblique arytenoid, and transverse arytenoid.
The lateral or vertebral group is made up of the anterior, middle, and posterior scalene muscles. Their primary function is the unilateral bending of the neck.
These muscles can be divided into three categories:
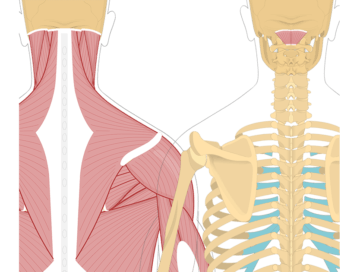
- Superficial muscles: Trapezius, splenius capitis, and splenius cervicis.
- Deep muscles: Cervical transversospinalis muscles, including semispinalis capitis, semispinalis cervicis, and multifidus cervicis.
- Deepest muscles: Suboccipital muscles, interspinales cervicis, and intertransversarii colli.
These muscles are incredibly diverse and can be organized into seven groups based on their specific functions:
- Extraocular muscles, responsible for moving the eyeballs in different directions.
- Superficial muscles of the head, further divided into epicranial, extrinsic auricular, and facial muscles (muscles involved in facial expression).
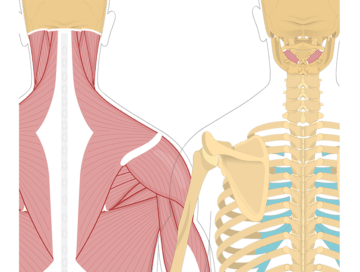
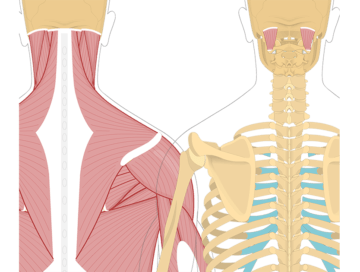
The rectus capitis posterior minor is a small muscle located at the back of the neck. It runs from the base of the skull to the upper vertebrae of the neck (atlas). The primary function of the rectus capitis posterior minor is to extend and rotate the head.
The obliquus capitis inferior is a muscle located at the back of the neck. It runs from the spine to the base of the skull. The primary function of the obliquus capitis inferior is to rotate and laterally flex the head. It plays a role in turning the head to the same side and bending it sideways.
The obliquus capitis superior is a muscle located at the back of the neck. It runs from the spine to the base of the skull. The primary function of the obliquus capitis superior is to rotate and laterally flex the head. It plays a role in turning the head to the opposite side and bending it sideways.
The rectus capitis posterior major is a muscle located at the back of the neck. It runs from the spine to the base of the skull. The primary function of the rectus capitis posterior major is to extend the head, allowing you to look upward. It also plays a role in stabilizing the head and neck during various movements.
The semispinalis capitis is a muscle located in the back of the neck and upper back. It runs from the upper thoracic spine to the base of the skull. The primary function of the semispinalis capitis is to extend and rotate the head. It plays a role in maintaining proper head posture and is involved in various head movements.
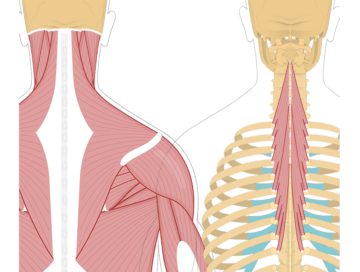
The semispinalis cervicis is a muscle located in the back of the neck. It runs from the upper thoracic spine to the upper cervical vertebrae. The primary function of the semispinalis cervicis is to extend and rotate the neck.
Semispinalis Thoracis
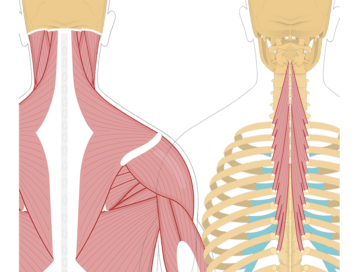
The semispinalis thoracis is a muscle located in the upper and middle back region. It runs from the lower thoracic spine to the upper thoracic spine. The primary function of the semispinalis thoracis is to extend and rotate the spine.
The splenius capitis is a muscle located in the back of the neck. It runs from the upper thoracic spine to the base of the skull. The primary function of the splenius capitis is to extend, rotate, and laterally flex the head.
The splenius cervicis is a muscle located in the back of the neck. It runs from the upper thoracic spine to the upper cervical vertebrae. The primary function of the splenius cervicis is to extend, rotate, and laterally flex the neck.