Back Muscles
- the trapezius
- latissimus dorsi
- levator scapulae
- rhomboids
- serratus posterior
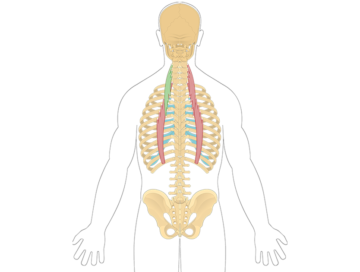
The intrinsic back muscles are organized into three layers:
- Superficial layer: splenius muscles, erector spinae muscles
- Deep layer: transversospinales (including semispinalis, multifidus, and rotatores)
- Deepest layer: interspinales and intertransversarii muscles
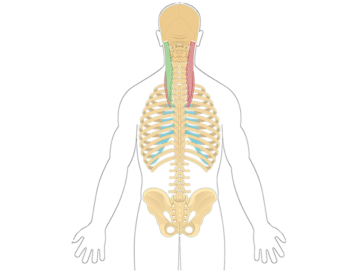
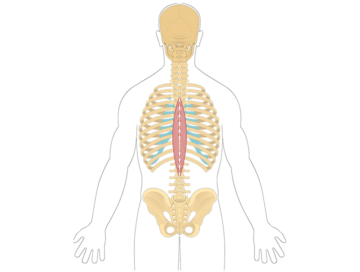
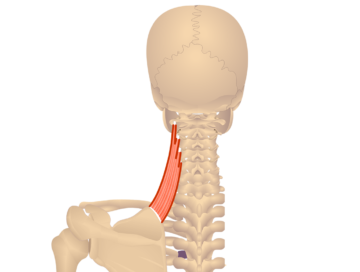
The iliocostalis cervicis is a muscle located in the back and neck region. It is part of the erector spinae muscle group, which helps extend and laterally flex the spine. The iliocostalis cervicis specifically supports the neck and upper back by assisting in movements such as tilting the head backward and sideways.
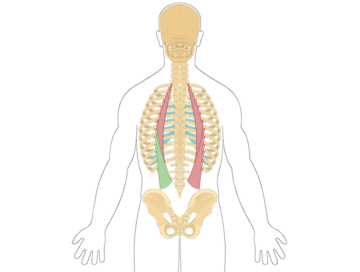
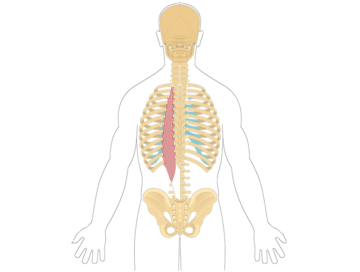
The iliocostalis lumborum is a muscle located in the lower back. It is part of the erector spinae muscle group, which helps extend and laterally flex the spine. The iliocostalis lumborum specifically supports the lumbar spine and assists in movements such as bending backward and sideways.
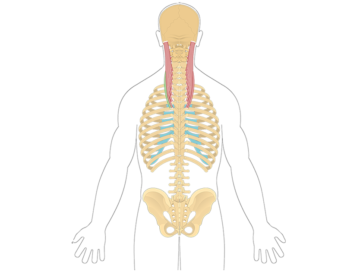
The iliocostalis thoracis is a muscle located in the mid to upper back region. It is part of the erector spinae muscle group, which helps extend and laterally flex the spine.
The longissimus capitis is a muscle located in the back of the neck. It is part of the erector spinae muscle group, which helps extend and laterally flex the spine.
The longissimus cervicis is a muscle located in the back of the neck. It is part of the erector spinae muscle group, which helps extend and laterally flex the spine.
The longissimus thoracis is a muscle located in the mid to upper back region. It is part of the erector spinae muscle group, which helps extend and laterally flex the spine.
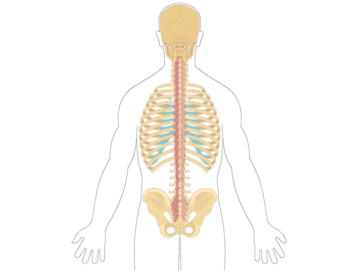
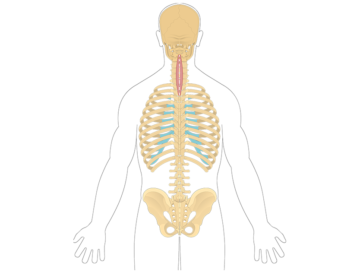
The multifidus is a muscle group located in the lower back region. It plays a crucial role in stabilizing and supporting the spine, providing protection and control during various movements. The multifidus helps with spine extension, rotation, and lateral flexion, contributing to overall spine stability and posture.
The spinalis cervicis is a muscle located in the neck region. It is part of the erector spinae muscle group, which helps extend and laterally flex the spine.
The spinalis thoracis is a muscle located in the mid to upper back region. It is part of the erector spinae muscle group, which helps extend and laterally flex the spine. The spinalis thoracis specifically supports the thoracic spine and assists in movements such as arching the back and bending sideways.
The quadratus lumborum is a muscle located in the lower back on both sides of the spine. It plays a key role in stabilizing the lower back and is involved in lateral flexion, allowing you to bend sideways.
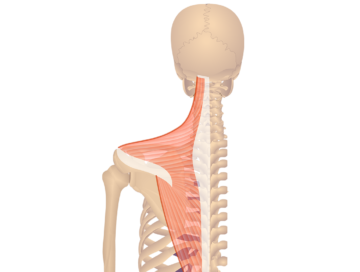
The trapezius is a large, triangular muscle located in the upper back and neck region. It plays a crucial role in moving and stabilizing the shoulder blades, allowing you to raise and lower your shoulders, as well as retract and rotate them. The trapezius muscle is involved in various movements, such as shrugging, pulling, and maintaining upright posture.
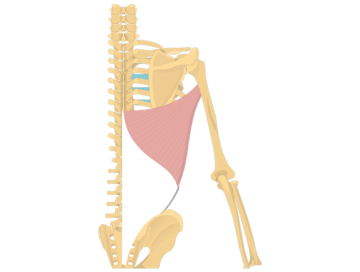
The latissimus dorsi, commonly known as the “lats,” is a large, flat muscle located in the middle and lower back. It plays a vital role in shoulder adduction, bringing the arm down and towards the body, as well as shoulder extension, pulling the arm backward.
The levator scapulae is a muscle located at the back and side of the neck. It plays a crucial role in elevating the scapula (shoulder blade), allowing you to shrug your shoulders upward. The levator scapulae muscle is involved in various movements of the shoulder and neck and helps maintain proper posture.
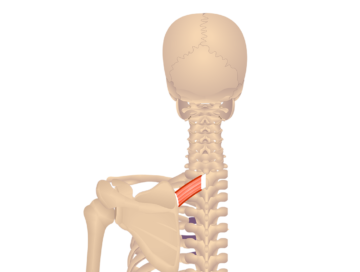
The rhomboid major is a muscle located in the upper back, between the spine and the scapula (shoulder blade). It works together with the rhomboid minor to retract and stabilize the scapula, pulling it towards the spine.
The rhomboid minor is a small muscle located in the upper back, between the spine and the scapula (shoulder blade). It works together with the rhomboid major to retract and stabilize the scapula, pulling it towards the spine.