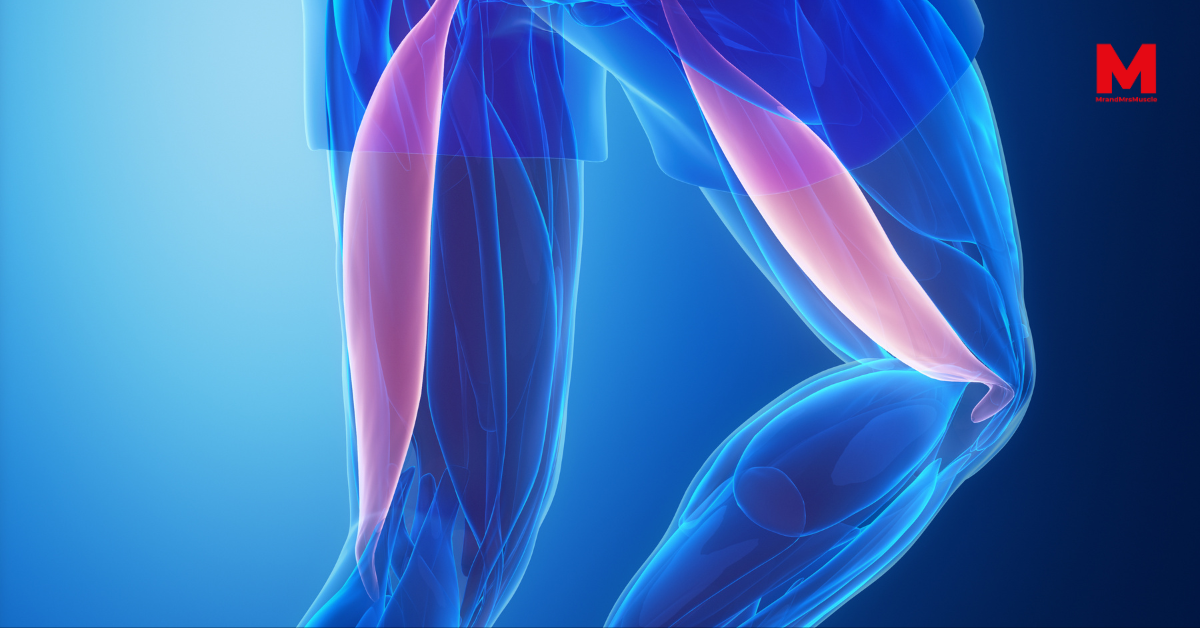
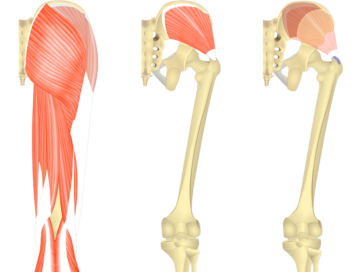
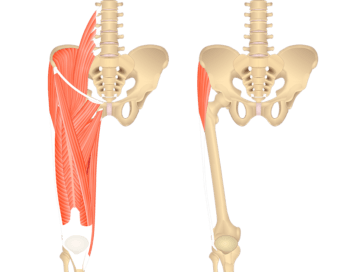
Posterior Thigh Muscles
In the back of the thigh lie the muscles of the posterior compartment, commonly referred to as the hamstrings.
This group is comprised of just three muscles:
- Biceps femoris
- Semimembranosus
- Semitendinosus
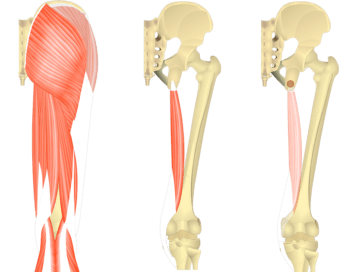
The semimembranosus is a muscle located at the back of the thigh. It is one of the three muscles that make up the hamstring group. The primary function of the semimembranosus is to flex the knee joint, allowing you to bend your leg at the knee. It also plays a role in extending the hip joint, moving the thigh backward, and stabilizing the knee during various movements.
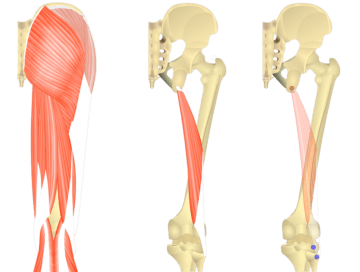
The semitendinosus is a muscle located at the back of the thigh. It is one of the three muscles that make up the hamstring group. The primary function of the semitendinosus is to flex the knee joint, allowing you to bend your leg at the knee.
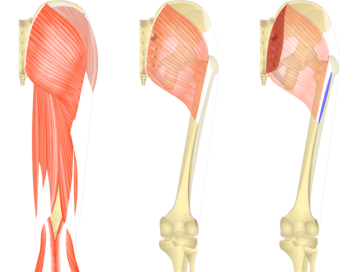
The biceps femoris is a muscle located at the back of the thigh. It is one of the three muscles that make up the hamstring group. The biceps femoris has two heads: the long head and the short head. The primary function of the biceps femoris is to flex the knee joint, allowing you to bend your leg at the knee.
The gluteus maximus is the largest muscle in the buttocks. It is a powerful muscle that plays a significant role in hip extension, allowing you to move your thigh backward. The gluteus maximus also assists in hip abduction, which involves moving the thigh away from the midline of the body.
The gluteus medius is a muscle located in the buttocks. It is situated above the gluteus maximus. The primary function of the gluteus medius is to abduct the hip, which means moving the thigh away from the midline of the body.
The gluteus minimus is a muscle located in the buttocks, beneath the gluteus medius. The primary function of the gluteus minimus is to assist in hip abduction, which means moving the thigh away from the midline of the body. It also plays a role in stabilizing the pelvis during walking and other weight-bearing activities, contributing to maintaining balance and proper alignment of the hips and spine.
The piriformis is a muscle located in the buttocks, deep beneath the gluteal muscles. The primary function of the piriformis is to externally rotate and stabilize the hip joint. It also plays a role in abducting the hip, moving the thigh away from the midline of the body.
Quadratus Femoris Muscle
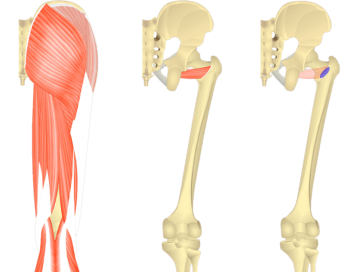
The quadratus femoris is a muscle located in the buttocks, deep beneath the gluteal muscles. The primary function of the quadratus femoris is to laterally rotate the hip joint, turning the thigh outward. It also plays a role in stabilizing the hip during various movements, such as walking, running, and standing.
The tensor fasciae latae (TFL) is a muscle located in the outer hip region. It runs along the iliac crest (the bony prominence of the hip) and inserts into the iliotibial (IT) band. The primary function of the TFL is to flex, abduct, and internally rotate the hip joint. It plays a role in stabilizing the pelvis during walking and other weight-bearing activities, as well as providing tension to the IT band, which helps with lateral stabilization of the knee.